Fix Any 1995 Ford F150 Starter Issue with Wiring Diagrams
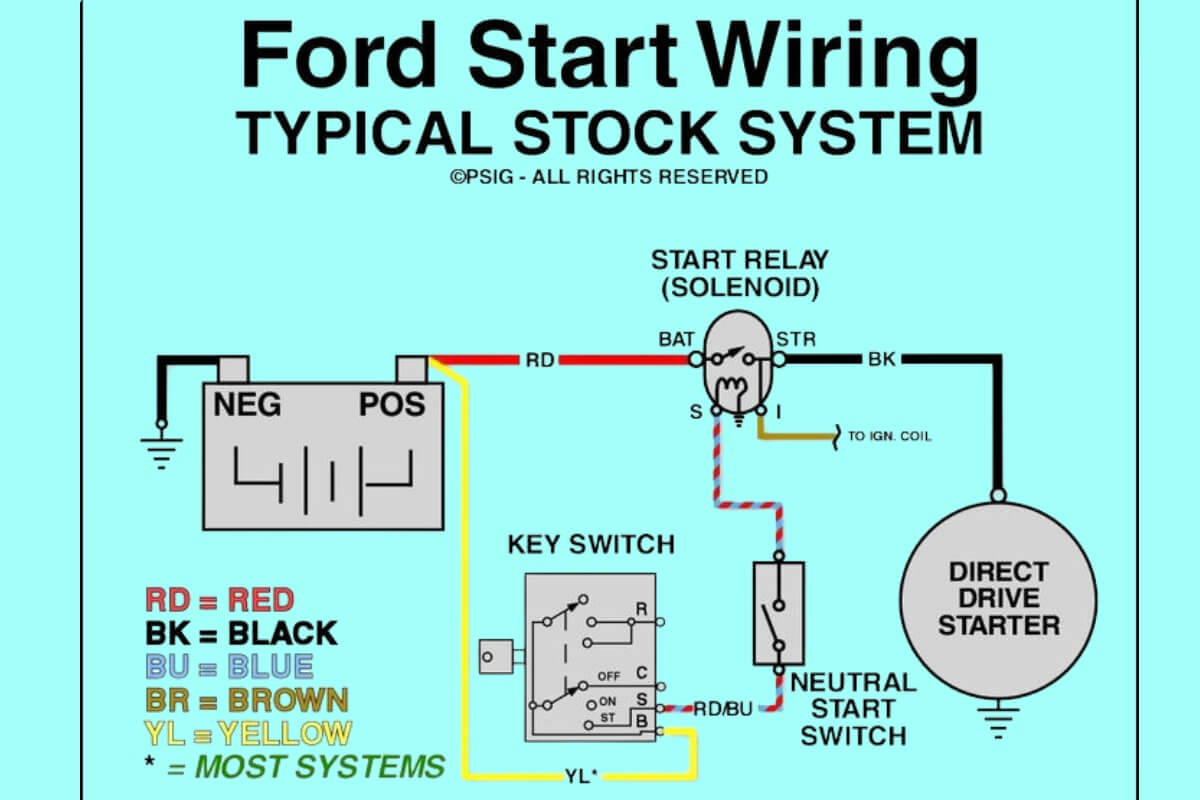
So you hop into your 1995 Ford F150, turn the key in the ignition switch, and instead of the satisfying roar of your truck starting up, you hear an ineffective clicking or perhaps nothing at all. Not great. Or maybe the engine slowly cranks over with a grinding sound before catching. What gives?
Can properly reading and diagnosing the 1995 F150’s starter and solenoid wiring diagram get your truck back up and running?
The short answer is – yes! While starter issues can be incredibly frustrating, understanding the starter relay, starter solenoid, and related circuits in the wiring diagram will help you systematically track down and fix the problem.
In this post, we’ll cover everything you need to know about using wiring diagrams to troubleshoot and remedy starter problems on the 1995 F150, including:
- How the different starter components work and connect together
- Tracing the starter wiring diagram on a 1995 Ford F150 step-by-step
- Diagnosing specific symptoms like click-no-start and slow cranking
- Replacing damaged starter parts like the motor or solenoid
- Best practices for preventative electrical maintenance
So let’s dive under the hood and pinpoint why your 1995 Ford truck is having issues turning over!
1995 Ford F150 Starter Solenoid Wiring Diagrams
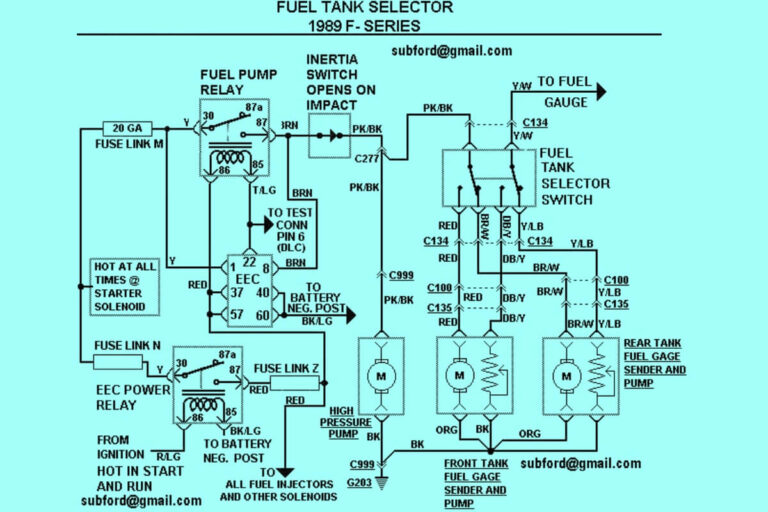
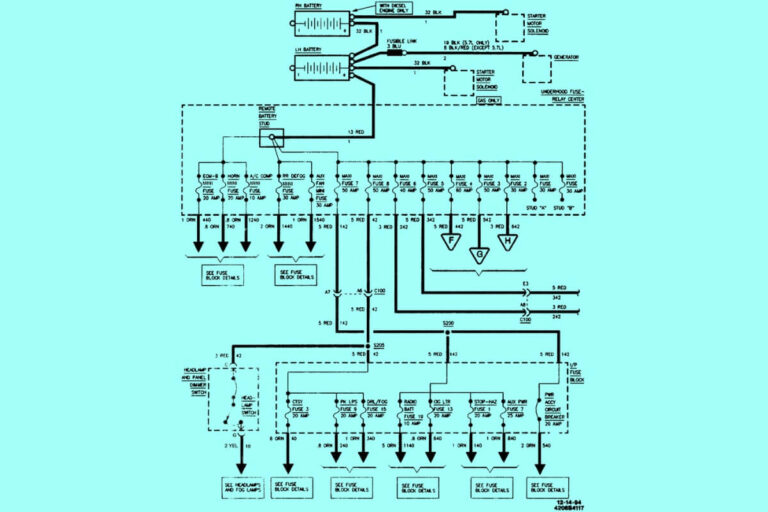
Diagram 1:
Diagram 2:
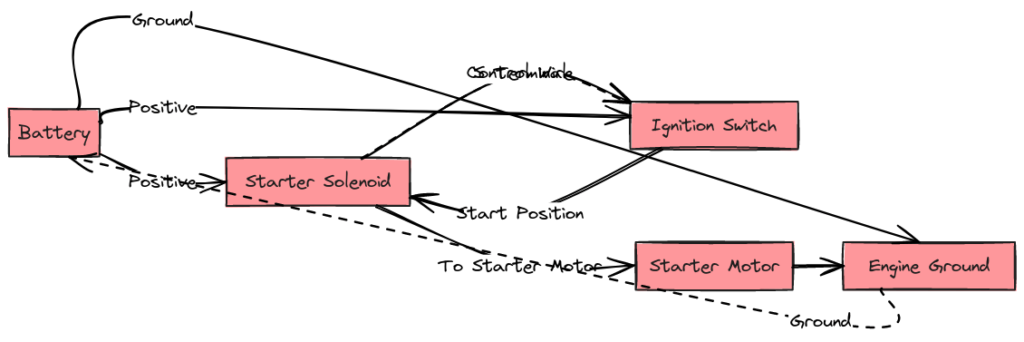
Diagram 3:
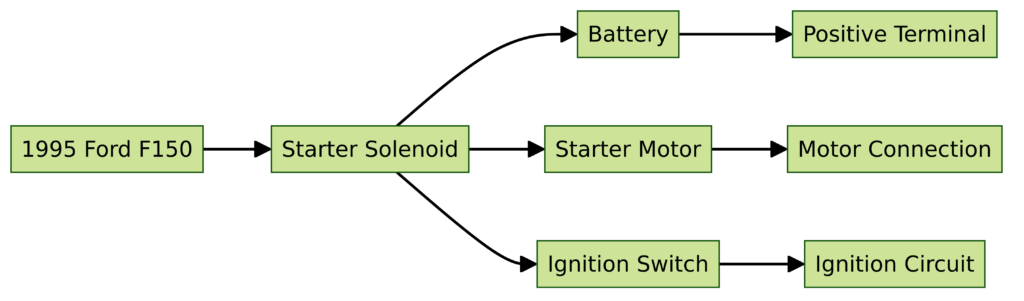
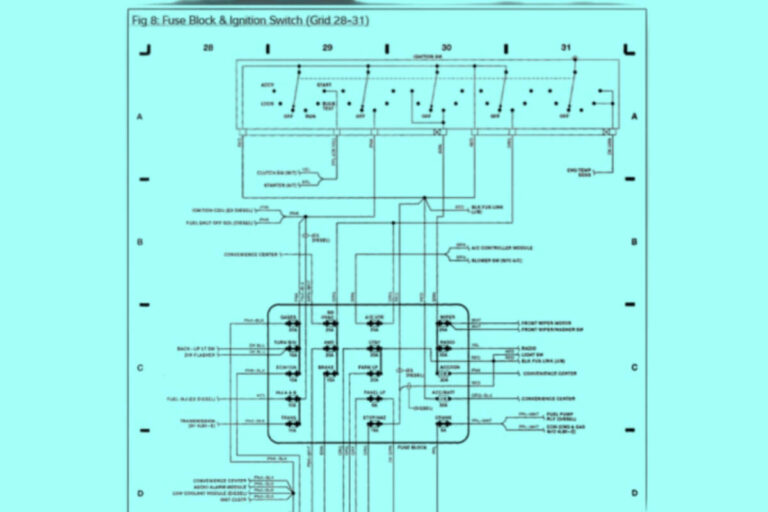
Diagram 4:
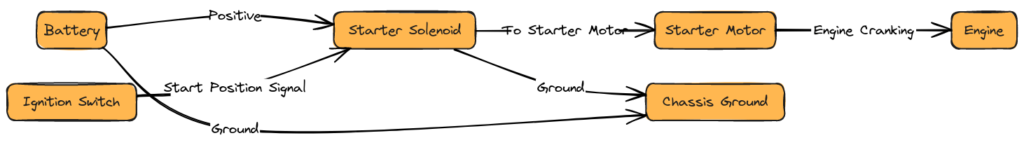
Diagram 5:

Understanding Starter System Components and Operation
Before jumping straight into the wiring, having a basic working knowledge of the key parts in your truck’s starter system is helpful for contextualizing how everything interacts. Here are the main players:
The Starter Motor
Mounted along the lower portion of the engine, the starter motor is responsible for physically cranking the engine to get it spinning on start-up. It is essentially a high-torque electric motor that engages with the flywheel via a drive gear when powered on.
Proper electrical connections, wiring, and voltage supply are critical for enabling starter motor operation.
The Starter Solenoid
The starter solenoid serves as a switch that controls power flow from the battery to the starter motor, allowing high amp loads to be turned on/off while using lower current at the ignition switch.
It uses an electromagnet to physically pull a plunger that connects the starter motor circuit to the battery when powered on. Faulty solenoids are a common starter issue.
The Ignition Switch + Circuit
The ignition switch and related wiring work together to activate the full starter system. Turning the key closes a circuit that sends voltage through various connections and ultimately energizes the starter solenoid and motor.
Problems with the switch contacts, ignition circuit wires, or connections can prevent starter activation entirely.
Here is a simplified sequence to visualize the process when you go to start your 1995 F150:
- Insert key and turn ignition switch to “Start” position
- Ignition switch circuit closed, power flows to activate starter relay
- Starter relay closes and sends power to small control circuit on starter solenoid
- Solenoid coil energized, pulls plunger to connect battery voltage to starter motor
- Motor cranks engine to begin start sequence
So in summary – the ignition circuit triggers a relay and starter solenoid that then engages the motor. Now let’s see how this looks in wiring diagram form!
Tracing and Understanding 1995 Ford F150 Starter Wiring Diagrams
Since starters contain various interconnected components, manufacturers provide wiring diagrams illustrating the electrical circuits in detail. Here is a sample starter wiring diagram from a 1995 F150:
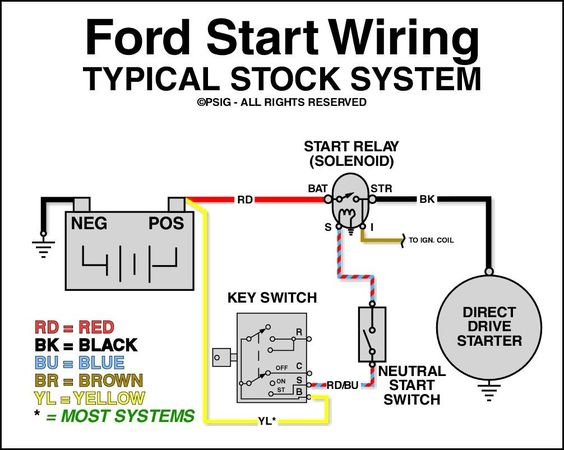
At first glance, diagrams with their mess of lines, colors, symbols, and labels can seem overwhelming.
But don’t worry! We’ll demystify things step-by-step:
Power Sources – Battery, Main Cables
The diagram will display power sources like the battery + and – terminals, along with thick cables carrying starter current.
Inspection should confirm clean, tight battery cable clamps for reliable flow. Voltage drop testing the heavy cables can check for resistance issues.
Ignition Switch Circuit
Thinner trigger wires that activate based on ignition switch position will be shown running to a 30 or 50 amp starter relay that is normally inline somewhere.
An broken ignition circuit wire or faulty relay causes click-no-start. Verify continuity and relay engagement.
Solenoid Activation Circuit
A smaller gauge wire provides power from the relay to the integrated starter solenoid. This circuit pulls the internal plunger in the solenoid when energized, allowing full battery current to reach the motor terminals.
If this control wire is disconnected or the relay output is dead, the solenoid won’t activate.
Motor Circuits
The starter motor itself has a thick positive cable coming from the battery-connected solenoid terminal that provides cranking current when pulled in. The motornegative lead goes to ground.
Resistance on these cables or internally on the motor windings can cause slow cranking.
Here is an example flow through the full circuit showing activation stages:
- Ignition switch turned → Powers control circuit through relay → Relay engaged
- Relay output sends current to solenoid activation wire circuit → Solenoid coil pulls in internal plunger
- Plunger connects battery positive cable to starter motor → Motor cranks engine
- Key released → relay, solenoid and motor circuit opened → starter disengages
Analyzing the types of connections and system progression as shown on the diagram allows systematic diagnosis of faults. Now let’s look at interpreting specific symptoms.
Diagnosing 1995 Ford F150 Starter Issues
Many starter problems on the 1995 F150 produce common symptom patterns that can point to certain wiring faults:
Starter Rapid Clicks But Doesn’t Crank
If you turn the ignition key and just hear a rapid click click click sound from the starter area without the engine cranking over, there are a few possible explanations:
- Battery is very weak and voltage drops too low on crank attempt. Check battery state of charge and voltage.
- Loose or dirty battery cable connections are preventing sufficient current to the starter. Trace and clean connections.
- Ignition switch circuit is not closing properly or relay fault is preventing solenoid activation wire from energizing. Use diagram to verify relay operation and control circuit continuity.
- Internal pull-in coil failure on the starter solenoid. Bypass solenoid with screwdriver test to isolate root cause.
Any breaks in the starter activation circuits will typically produce the rapid click as things attempt to engage but fail. Methodically verify each segment of the diagram at a time.
Starter Cranks Slowly or Makes Grinding Noises
If your F150’s starter is turning over the engine slowly or making terrible grinding sounds in the process, it points to issues in the high current sections:
- Inadequate current supply due to excessive resistance on deteriorated motor windings or solenoid contacts not fully closing. Measure voltage drop and current flow to the motor during cranking.
- Worn drive gear teeth that are not properly meshing with the flywheel. Gear damage causes grinding and struggles to spin motor.
- Low battery charge struggling to provide sufficient heavy cranking current due to aging battery or bad cell(s). Check voltage and battery load test.
Evaluating these circuits covered on the diagram will uncover the root deficiency.
There are other common issues tied to external factors like a faulty neutral safety switch preventing starter operation or ignition switch malfunctions. But the starter system diagram will help reveal or eliminate these possibilities.
Next let’s discuss replacement options when you isolate internal starter components that are damaged and causing problems.
Replacing a Bad 1995 Ford F150 Starter or Solenoid
If you have tested related circuits on the diagram but determine the starter itself is bad, replacement is needed. Here is an overview of what’s entailed for the common failure points:
Replacing the Starter Motor
Physically removing the starter on the 1995 F150 involves removing bolts securing it along the engine and also disconnecting wiring. Caution must be used not to damage existing wiring during removal/install.
Once removed, carefully compare connectors and mounting points between old and new replacement starter to ensure proper alignment. Install is reverse of removal, taking care with electrical connections and mounts. Average cost for a new starter motor is $150-200.
Replacing the Starter Solenoid
Located on top of the starter housing itself, replacing solenoids is a simpler job without much disassembly. Just disconnect the main battery power lead, then the two small activation wire spade connectors. Remove old solenoid and transfer wiring to new unit, reinstalling wires and main battery lead last. Beware arcing from battery cable. Expect to pay $70-88 for a quality new starter solenoid.
In both cases, take care with wiring connections. Reference diagram as needed to confirm proper layout. With fresh components, the starter should crank strongly again!
Preventing Future 1995 Ford F150 Starter Problems
Aside from addressing acute starter failures, some proper proactive electrical maintenance steps can prolong the life and performance of your 1995 F150’s starting system. Consider these best practices:
- Clean battery cable connections at terminals and along run to ensure minimal resistance
- Load test the battery annually, consider replacing every 4-5 years
- Inspect ignition switch contacts for corrosion and smooth operation
- Check belt tension for starter pinion and flywheel contact
- Listen for grinding sounds on startup indicating pending gear wear
- Consider upgrading to heavy duty starter components designed for longevity
Keeping up on these basic system checks, along with reviewing the wiring diagram for any starter-related problems, goes a long way towards preventing being left stranded with no-start issues down the road!
Conclusion and Summary
Getting stuck with a no-start 1995 Ford F150 that just uselessly clicks instead of firing up is hugely frustrating. But armed with the starter motor and solenoid wiring diagram for your truck, methodically tracking down the underlying electrical issue causing failure is straightforward.
Whether finding problems with battery connections, tracing ignition switch or relay circuits, replacing worn brushes in the motor, or testing solenoid windings, understanding the routes of power flow makes diagnosis logical. Combining diagram analysis with basic voltage, resistance and continuity testing will uncover any hidden gremlins.
With a quality replacement starter or solenoid installed and preventative maintenance followed, your 1995 Ford F150 will crank vigorously again when turning the key. Here’s to escaping the dreaded click-no-start scenario for good!