Ford Starter Solenoid Wiring Diagram: Fix your Issues
Having trouble starting your Ford vehicle? Issues with the starter solenoid or related wiring can leave you stranded. This in-depth guide will walk through diagnosing Ford starter and solenoid problems, provide tips on reading wiring diagrams, and give step-by-step instructions on testing and replacing the starter solenoid.
So how do you properly troubleshoot Ford starter solenoid wiring problems? The key is methodically testing components like the battery, starter relay, and ignition circuit to isolate the issue. Compare symptoms against a wiring diagram to pinpoint solenoid failures. Swap in a new solenoid or examine the harness for damage. With some basic tools and patience, you can get your Ford back up and running.
We’ll cover the common Ford starter and solenoid issues, explain how to test the solenoid with a multimeter, provide terminal diagrams, wire color codes, and step-by-step diagnosis procedures. You’ll also find tips for installing a new solenoid, wiring modifications, links to Ford-specific forums, and more. Let’s dive in!
Understanding Starter and Solenoid Components
Before testing the solenoid, it helps to understand how the key starter components function in Ford vehicles:
- Starter Motor – Drives the engine to turn over when starting. Engages via a bendix gear when powered on.
- Solenoid – Electromagnetic switch that engages starter when ignition turned.
- Ignition Switch – Sends power to solenoid/starter when key turned to Start.
- Battery – Provides high current to starter motor via thick battery cables.
- Relay – Some vehicles use a starter relay instead of sending ignition switch power directly to solenoid.
Voltage from the battery flows through multiple safety switches, before getting to the ignition switch. Turning the key closes that circuit.
On most Ford vehicles, that power goes straight to the starter solenoid S terminal, activating the electromagnets to close contacts and power the motor.
The solenoid acts as a high current switch, allowing the small current from the ignition circuit to control the high amp starter.
Understanding this flow of electricity through the starter circuit components provides context for systematic troubleshooting.
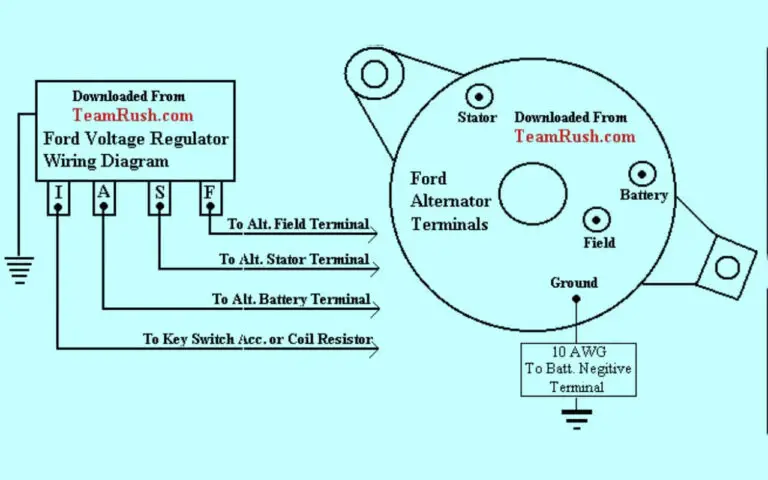
Ford Starter Solenoid Wiring Diagram
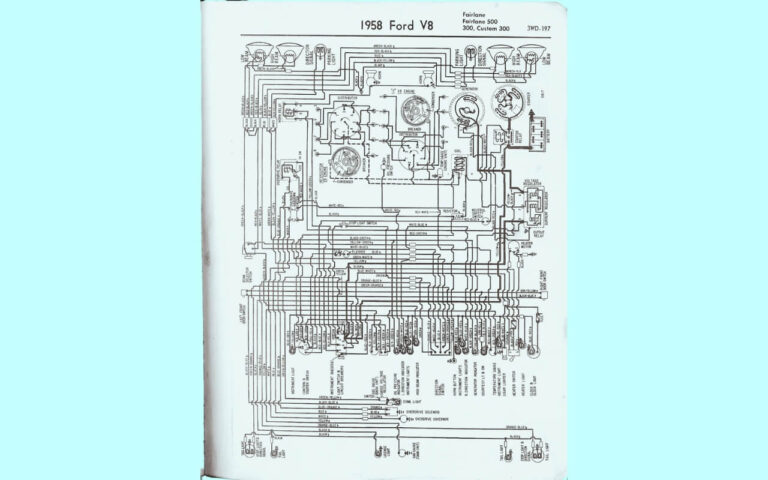
Diagram 1:
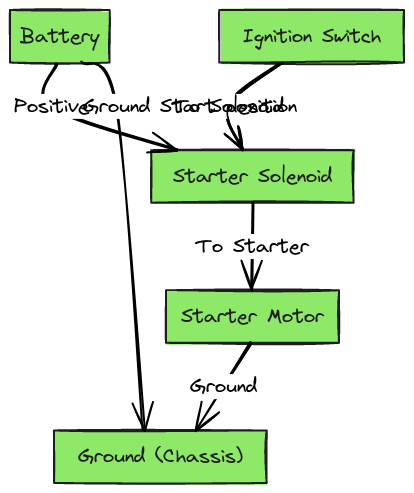
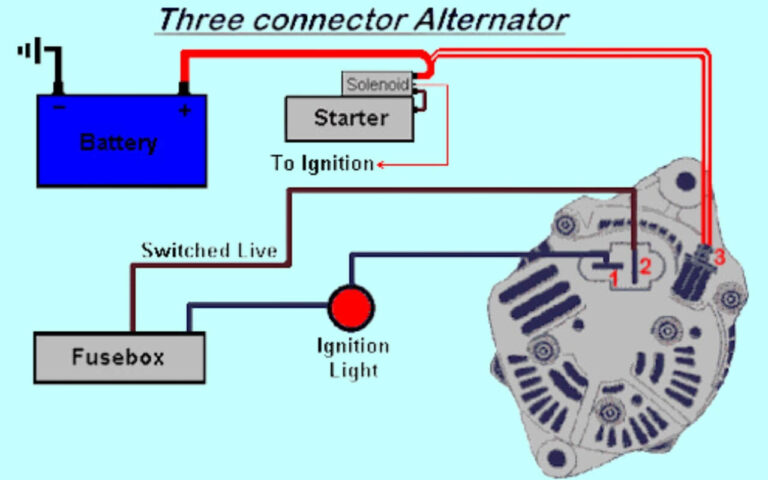
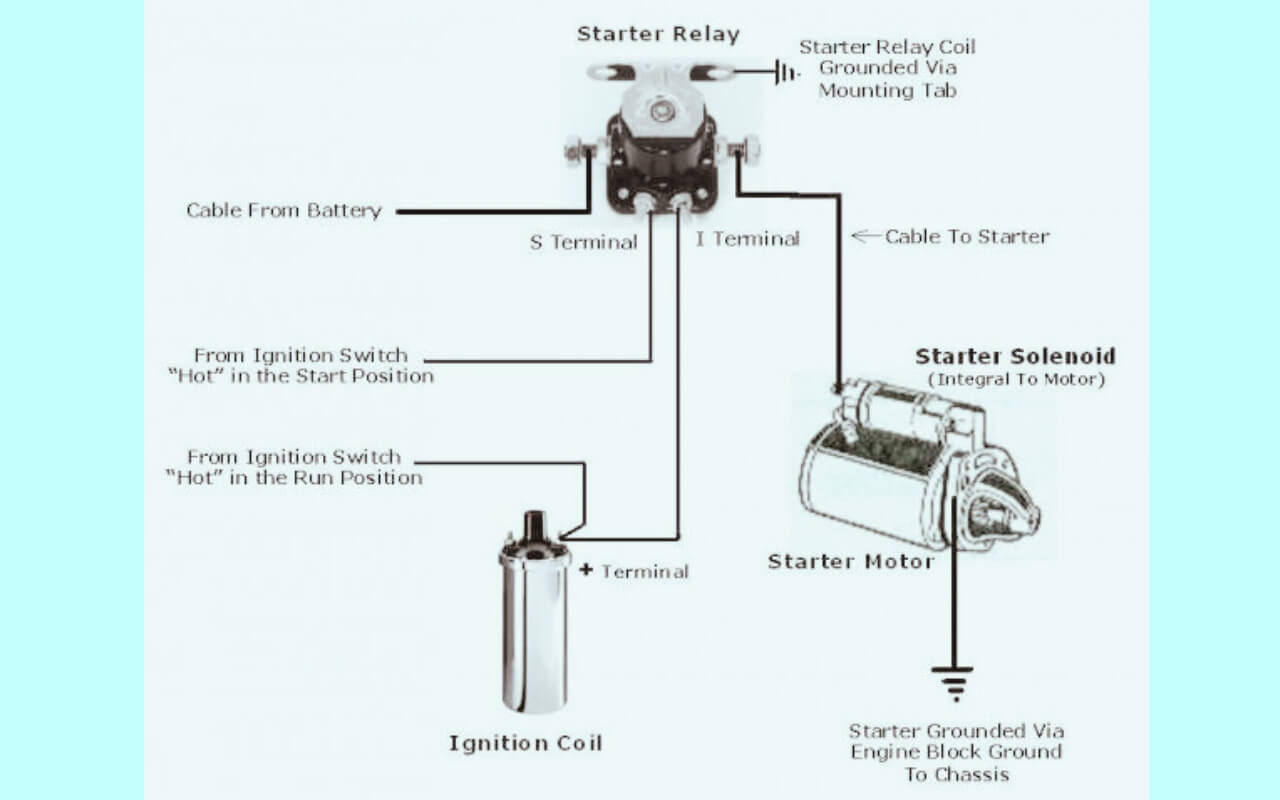
Diagram 2:
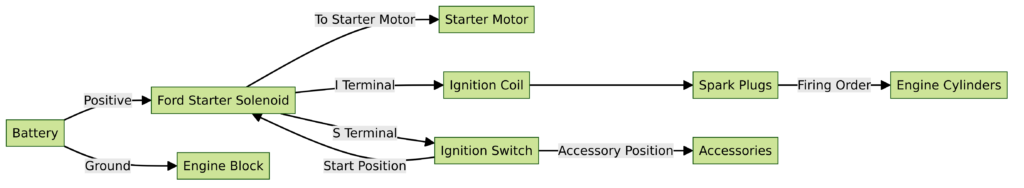
Diagram 3:
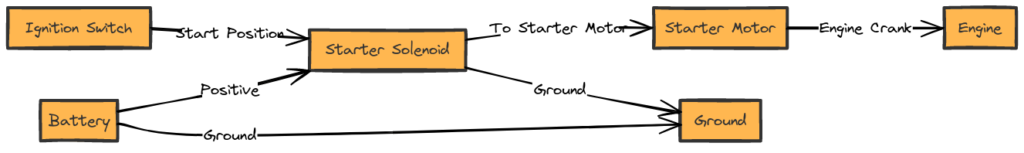
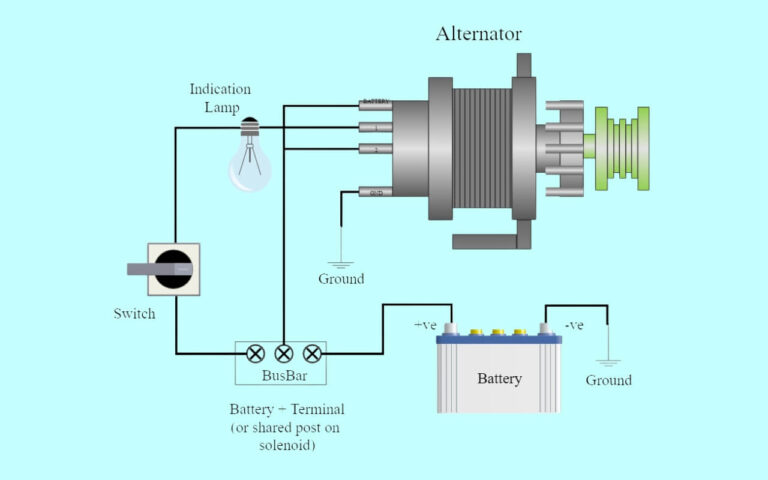
Diagram 4:
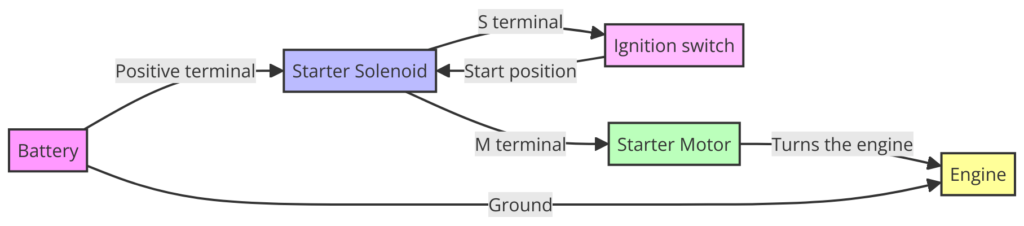
Common Ford Starter and Solenoid Problem Symptoms
Before assuming the solenoid failed, consider what common starter and solenoid problem symptoms typically look like in Ford vehicles:
- No cranking when turning key – Solenoid clicks but starter doesn’t turn. The bendix gear won’t engage.
- Intermittent operation – Starter cranks slowly or only under certain conditions. May die suddenly.
- Grinding noise – Bendix gear stays engaged with flywheel as engine runs.
- Chattering/Shuddering – Starter engages then quickly disengages while cranking.
- Solenoid stays engaged – Key returns to Run but starter keeps cranking battery down.
Note these symptoms as we walk through systematic troubleshooting techniques. Compare to what your Ford does when trying to start.
With an overview of the components and possible symptoms, let’s look at testing the solenoid operation itself.
Testing the Ford Starter Solenoid
Before condemning the solenoid, it helps to test and validate if it’s truly at fault. Use a multimeter to check the following:
- Battery Voltage – At least 12v at solenoid B+ terminal with key off
- Power Into Solenoid – 12v at S terminal when key turned to Start
- Continuity Check – Resistance across posts with power applied
- Ground Check – Clean ground from solenoid body to battery negative
A bad ground, low battery voltage, or no power to the S terminal can prevent proper solenoid operation.
If testing shows 12v into the solenoid but no output when activated, focus diagnosis on the solenoid itself. See the wire diagram in the next section.
Reading a Ford Starter Solenoid Wiring Diagram
For visual learners, consulting a wiring diagram speeds up diagnosing no-start issues. Here is a quick reference solenoid terminal diagram:
The large terminals connect the battery power and motor wires. The small S terminal activates the solenoid when 12v is applied by the ignition switch.
Wiring color codes vary across Ford models but often follow conventions below:
- Red – Ignition/Accessory power
- Yellow – Starter motor to solenoid output
- Black – Ground wires
- Orange – Sometimes for battery to solenoid power
- Green – Alternator wiring
See your vehicle-specific diagram but these typical codes help trace starter circuits.
Now let’s step through a complete troubleshooting procedure.
Step-by-Step Starter Diagnosis on Fords
With the basics covered, here is a methodical process to diagnose Ford starting problems:
1. Confirm Battery Voltage
Loose battery terminals or a dead battery will prevent proper starter operation.
- Turn on headlights and accessories to load test battery.
- Check voltage at battery posts and at solenoid B+ terminal.
Charging or jump starting may be required before further diagnosis.
2. Check Battery Cables & Terminals
High current flows through the thick battery cables to the starter.
- Verify cable connections are clean and tight at the terminals.
- Loose connections can cause intermittent contact or high resistance.
3. Listen for Solenoid Clicks
Turn the key to the Start position and listen for a click at the starter.
- No click – no power to solenoid or bad ground. Proceed to next steps.
- Click but no crank – Focus on solenoid failure or stuck starter motor.
4. Check Ignition Switch Power
Test for power at the solenoid S terminal with key in Start.
- Probe the terminal with a multimeter set to volts.
- If no voltage during cranking, problem is in the ignition circuit.
5. Check Starter Fuses/Relays
Many vehicles have a separate relay or fuse for the starter circuit.
- Consult wiring diagram to locate any fuses and relays.
- Verify they have continuity or aren’t blown. Replace if bad.
6. Directly Power Solenoid S Terminal
To isolate control circuit issues, directly power the solenoid activation terminal.
- Use a jumper wire connected to the positive battery terminal.
- Touch other end to the S terminal briefly.
If starter spins normally, focus on the ignition switch or relay control circuits next. If issues remain, the solenoid or motor may be bad.
7. Tap Starter with Handle
If no click at all, a bad ground or seized motor can prevent solenoid engagement.
- Lightly tap the starter body with a wrench or handle while an assistant turns the key.
- This may free up stuck brushes or clean contact surfaces.
8. Check all Grounds
Clean, tight grounds are critical for high current flow.
- Verify starter body has good metal-to-metal contact to engine block.
- Engine or body ground straps should also be cleaned and checked.
Following these steps methodically will help isolate if the root cause is the battery, control circuits, solenoid, or starter.
Next let’s examine solenoid terminal functions.
Ford Starter Solenoid Terminal Functions
Referring back to our solenoid diagram, review the purpose and connections for each terminal:
- Battery (B+) Terminal – Power input from positive battery cable. Provides high current flow to activate electromagnets in solenoid and spin motor.
- Output Terminal – Where starter motor positive cable connects. Engages motor.
- Ground Terminal – Negative path to ground battery power after flowing through motor.
- S Terminal -Activation signal input from ignition switch circuit. Applies power to internals when ignition turned to Start. Launches plunger to close high current contacts.
- R Terminal – Optional terminal used for relay control in some vehicles. Ignition power goes here rather than directly to S terminal if equipped.
So the key solenoid terminals involved are the B+, output post, ground, and S terminal. The R terminal only applies if a relay is used.
Knowing each terminal’s function helps isolate problems during diagnosis.
Now let’s examine installing a new solenoid.
Installing a New Ford Starter Solenoid
Once determined that the solenoid has failed, replacing it is straightforward:
Parts and Tools Needed
Gather the following before replacing solenoid:
- New 12v Starter Solenoid – Ford OEM or Aftermarket
- Matching Solenoid Gasket/Seal if applicable
- Wrench/Socket Set
- Clean Rags
For accessibility, also raise and support the vehicle.
Removal Procedure
With access improved, now remove old solenoid:
- Disconnect negative battery terminal
- Label all wires and connections
- Clean loose debris/dirt around starter
- Disconnect solenoid wiring
- Remove starter mounting bolts
- Carefully detach solenoid
- Separate and clean mating surfaces
Installation Steps
Installing proceeds in reverse:
- Apply seal/gasket if supplied with new solenoid
- Set solenoid in place, install mounting bolts
- Attach all wires and terminals to matching posts
- Ensure solid contact at mounting surface
- Reconnect negative battery cable
Be meticulous when remounting wires to get original layout. Turn key to Accessory to confirm starter not engaging before fully reassembling.
And that covers replacement for a confirmed failed solenoid. But various Ford models can have unique wiring considerations.
Ford Starter Solenoid Wiring Modifications
Across different Ford model years, some have application-specific solenoid wiring:
Dual Solenoids – Some large truck or diesel starter arrangements use two separate solenoids. Both the control and motor circuits need properly wired.
Relay Triggered – As mentioned earlier, using a relay to trigger the solenoid separates control circuits. Check wiring diagram for differences.
Resistor Wire – Certain models need a ballast resistor wire going to the ignition circuit to prevent overvoltage to solenoid coil.
Upgraded Cables – High output alternators may require larger gauge B+ cables to handle increased current flow.
So be aware Ford starter solenoids do have some model-specific wiring considerations. Having the correct diagram is key if modifying circuits.
Next let’s cover some expert-level troubleshooting tips.
Expert Tips for Tricky Solenoid Diagnosis
Intermittently working solenoids or vague symptoms can make diagnosing tricky on Fords. Here are some advanced tips:
- Monitor voltage drops under load – Use a graphing multimeter to visualize drops indicating high resistance points in circuit.
- Wiggle test battery cables – Engine off, have assistant crank while wiggling cables to check for fluctuating voltage.
- Apply light voltage to S terminal – Using an adjustable power supply, slowly increase voltage to find drop-out point.
- Check solenoid plunger gap – A bent plunger rod may only engage partially depending on temperature and voltage.
- Inspect contacts for pitting – Heavy pin/contact wear can cause poor connections and heat damage.
- Consider pending sensor codes – Crank or cam sensors detecting engine rotation can affect activation.
- Review grounds with high current probe – Measures dynamic ground connection resistance under actual cranking loads.
While not always necessary, these tips help troubleshoot marginal component failures that show up only under certain conditions.
For additional advice to complement your vehicle-specific wiring diagrams, tap into Ford communities online.
Ford-Specific Starter and Solenoid Troubleshooting Forums
With Ford’s extensive vehicle history, model-specific forums provide focused troubleshooting advice:
- F150forum – Popular site covering Ford trucks. Search starter or solenoid threads.
- FordTrucks – Enthusiast forums dedicated to Ford pickups.
- FordMuscleforums – Targeted more towards classic and high performance Fords.
- Reddit Ford – Browse Ford subreddit for DIY advice across models.
Reddit also has starter issue threads for the Ranger, Mustang, Focus, and other models.
These Ford communities, paired with your vehicle diagrams, offer an abundance of solutions for any starter or solenoid problem that arises.
Conclusion and Summary
Tracking down no-start conditions takes patience but methodically verifying each component will lead to the root cause.
Key takeaways when troubleshooting Ford starter solenoid wiring:
- Understand starter circuit component functions
- Note symptoms compared to possible failure modes
- Methodically isolate battery, switch, relay/fuse, solenoid, motor
- Consult vehicle-specific wiring diagrams
- Check critical voltages, grounds, terminal connections
- Consider modifications needed for specific configurations
- Leverage Ford communities for model-specific advice
With this overview of systematically diagnosing Ford starter and solenoid issues, you can confidently troubleshoot problems that leave you stranded.
Carefully work through each step outlined to safely restore starting function. Let us know in the comments if you have any tips to add or questions on resolving no-start issues for your Ford!