How to Replace a Circuit Breaker: Easy DIY Electrical Guide
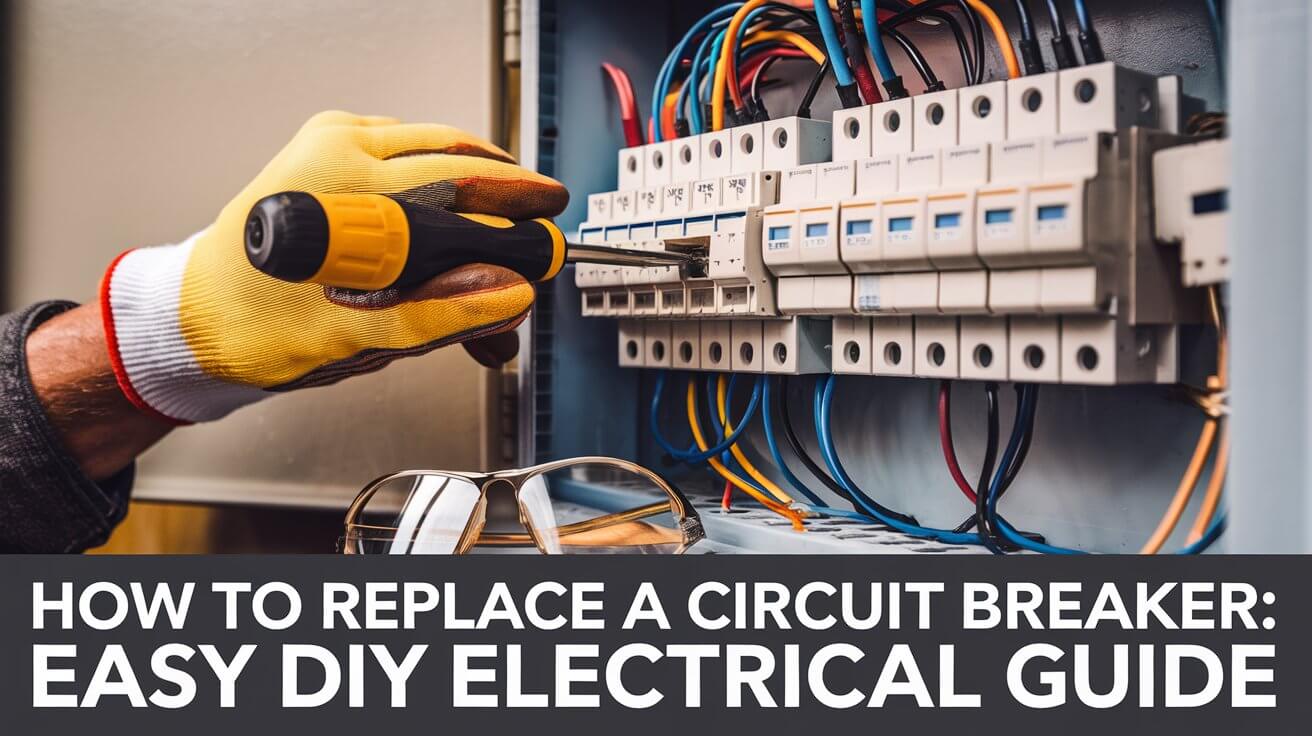
Replacing a circuit breaker may sound intimidating, but with the right tools and safety precautions, it’s manageable for homeowners. A faulty breaker can lead to power outages or safety risks, so knowing how to replace it can save you time and money. In this detailed guide, we’ll walk you through every step, from identifying the problem to installing a new breaker.
What Tools and Materials Are Required to Replace a Circuit Breaker?
Essential Tools
- Non-contact voltage tester – To confirm the circuit is off.
- Insulated screwdrivers – For unscrewing the panel cover and terminals safely.
- Wire strippers or pliers – To prepare wires for reconnection if needed.
- Flashlight or work light – In case the room goes dark during the process.
Materials
- Replacement breaker – Must match the brand, model, and amp rating of the old one.
- Electrical tape – For marking wires or securing connections.
- Rubber gloves and dry mat – For safety and insulation when working with live panels.
Preparing for the Replacement Process
When Should a Circuit Breaker Be Replaced?
Circuit breakers rarely need replacement unless they are faulty. Common signs include:
- Frequent tripping with no apparent cause.
- Inability to reset the breaker.
- Overheating or burning smell from the breaker panel.
- Physical damage like melted plastic or burn marks.
Additionally, you might replace breakers during an upgrade or renovation to meet code requirements, such as installing AFCI or GFCI breakers for added safety.
Safety Tips Before You Begin
Electrical repairs carry risks, so follow these safety steps:
- Turn off the main breaker before accessing the panel to disconnect power from branch circuits.
- Be aware that service lines (from the utility company) remain live even after switching off the main breaker.
- Use a voltage tester to confirm that all circuits are de-energized before handling wires.
Step-by-Step Guide to Replace a Circuit Breaker
Step 1 – Shut Off Main and Branch Circuit Breakers
- Turn off all individual breakers one by one. This reduces the risk of surges when power is restored.
- Finally, switch off the main breaker. This will cut power to the panel, but remember that the service lines may still carry live current.
Step 2 – Remove the Panel Cover
- Use an insulated screwdriver to remove the screws holding the breaker panel cover.
- Start by unscrewing the corners, leaving the middle screws until last to support the cover’s weight.
- Set the cover aside carefully without disturbing wires inside the panel.
Step 3 – Identify and Remove the Faulty Breaker
- Locate the faulty breaker and mark it with electrical tape to avoid confusion.
- Pull the breaker outward with gentle pressure. If it’s stuck, wiggle it slightly while avoiding contact with the bus bar (a conductive strip that remains live).
Step 4 – Disconnect the Wires
- Unscrew the terminal screw to disconnect the hot wire (usually black or red).
- If it’s a 240V breaker, disconnect both hot wires.
- For AFCI/GFCI breakers, also remove the neutral pigtail wire from the neutral bus bar.
Installing the New Circuit Breaker
Step 5 – Connect Wires to the New Breaker
- Ensure the new breaker is in the OFF position before connecting wires.
- Attach the hot wire(s) to the load terminal and tighten the screw securely.
- For AFCI or GFCI models, connect the neutral wire to the correct terminal and the pigtail to the neutral bus bar.
Step 6 – Insert the New Breaker into the Panel
- Align the new breaker with the panel’s bus bar.
- Press it firmly into place until it snaps securely.
Step 7 – Inspect and Replace the Panel Cover
- Check for loose wires or other issues inside the panel.
- Replace the panel cover, ensuring all screws are tight and even to avoid gaps.
Testing the New Breaker and Restoring Power
Step 8 – Turn On the Main and Branch Breakers
- Flip the main breaker back on, followed by the branch circuit breakers, one at a time.
- This gradual approach helps prevent sudden surges or arcing.
Step 9 – Perform a Voltage Test
- Use a voltage tester to ensure the new breaker is working properly.
- Test appliances and outlets on the replaced circuit to confirm everything is functioning as expected.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
- Breaker trips immediately: This might indicate a short circuit or an overloaded circuit.
- New breaker won’t fit: Ensure the breaker matches the panel in terms of brand and amp rating.
- Power not restored: Double-check wire connections, and make sure no terminals are loose. If the issue persists, consult a licensed electrician.
When to Call a Professional Electrician
Some situations require expert handling, such as:
- Replacing the main breaker: This involves working with high-voltage service lines.
- Upgrading to AFCI/GFCI panels: These installations may need electrical code compliance.
- Handling solar panels or generators: Specialized knowledge is required to manage backup power systems safely.
FAQs About Circuit Breaker Replacement
How Much Does It Cost to Replace a Circuit Breaker?
- Breaker cost: $10–$170, depending on type and amp rating.
- Professional service: Hiring an electrician may cost between $150–$300 per breaker, including labor and materials.
How Long Does It Take to Replace a Circuit Breaker?
- Replacing a single breaker typically takes 30–60 minutes, provided you have the right tools and experience.
Conclusion
Replacing a circuit breaker is straightforward if you follow the right steps and take necessary precautions. This guide covers everything from tools required to troubleshooting tips. While it’s a task that many homeowners can manage, it’s important to know when to call a professional, especially for more complex electrical work. Regular inspections and upgrades can also prevent problems before they arise, ensuring your home’s electrical system runs smoothly and safely.