What is a Watt? Understanding Power Measurement and Usage

The watt (W) is a basic unit of power used to measure the rate of energy transfer. It plays a crucial role in everyday life, from determining the energy consumption of your household appliances to evaluating the output of engines and power plants. One watt is defined as one joule of energy transferred per second, providing a simple but powerful way to quantify how much energy is used or generated over time.
This article will dive deep into everything you need to know about watts, its origins, scientific significance, applications, and how understanding it can help you make more informed energy choices.
Historical Background of the Watt
The watt is named after James Watt, a Scottish engineer and inventor (1736–1819) who made significant improvements to steam engine technology. These enhancements played a pivotal role in the Industrial Revolution, revolutionizing industries like mining, manufacturing, and transportation.
James Watt did not invent the steam engine, but his improvements made it more efficient and practical for large-scale industrial use. His work directly impacted the amount of work machines could do, thus changing how engineers and scientists thought about power and energy transfer. The adoption of “watt” as a unit of power pays homage to his contributions to the field of engineering.
The unit became officially recognized in 1889 at the International Electrical Congress, and later, it was included in the International System of Units (SI).
Defining the Watt: The Science Behind It
Basic Definition of a Watt
At its core, a watt is a measure of power, defined as the rate at which energy is transferred or converted. One watt is equivalent to one joule per second. This simple definition makes it a useful unit across different scientific and engineering disciplines.
The formula for calculating watts is straightforward:
W = J/s
Where:
- W = Power in watts
- J = Energy in joules
- s = Time in seconds
SI Units for Watt
Watt is a derived unit in the International System of Units (SI). It’s constructed using other base SI units, such as kilograms (kg), meters (m), and seconds (s). More specifically, the watt can be expressed in terms of these units as follows:
W = kg·m²/s³
This means that watt quantifies how quickly energy is transferred or used in any system, whether mechanical, electrical, or otherwise.
Watts and Electrical Power
In the context of electricity, the watt is commonly used to measure how much energy an electrical device consumes or generates. This can be anything from light bulbs to large industrial machines. For most of us, watts are closely associated with the power ratings we see on home appliances, like microwaves or air conditioners, which tell us how much energy the device will use.
Examples of Common Appliances and Their Wattage
Here are some common examples of household appliances and their typical wattage ratings:
- Incandescent light bulb: 40W – 100W
- LED light bulb: 10W – 20W (same brightness as a 60W incandescent bulb)
- Microwave oven: 1000W – 1500W
- Refrigerator: 150W – 300W
- Air conditioner: 1000W – 3000W
These numbers show how wattage varies across different devices, and understanding them can help you manage energy consumption effectively.
Formula to Calculate Watts in Electrical Devices
For electrical devices, wattage is often calculated using the formula:
W = V × A
Where:
- W = Power in watts
- V = Voltage in volts
- A = Current in amperes
For instance, if a device uses 120 volts and draws 10 amps of current, the power consumption would be:
W = 120V × 10A = 1200W
This formula is handy for calculating the power usage of various devices, especially if you want to know how much electricity something consumes over time.
Difference Between Watt, Kilowatt, and Kilowatt-hour
What is a Kilowatt?
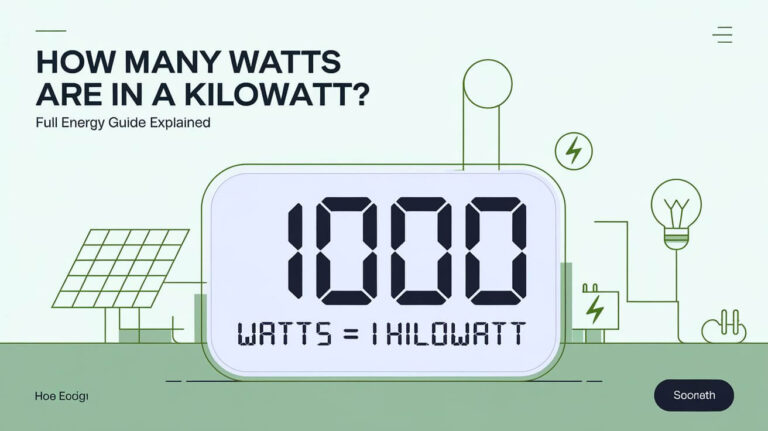
A kilowatt (kW) is simply 1,000 watts. This larger unit is often used when discussing electrical power generation or consumption on a larger scale. For instance, the output of a home solar panel or the power consumption of an air conditioning unit is typically measured in kilowatts.
For example:
- 1kW = 1000W
What is a Kilowatt-hour (kWh)?
While the watt measures power, the kilowatt-hour measures energy consumption over time. One kilowatt-hour is the amount of energy consumed when a device with a power rating of 1 kilowatt operates for one hour.
So, if you use a 1000-watt appliance for one hour, it consumes 1 kWh of energy.
This is the standard unit used by utility companies to bill customers for electricity usage. By understanding your device’s wattage and usage time, you can estimate how much energy you’re using and how it will impact your electric bill.
Application of Watts in Various Fields
Electric Power Generation
Watts are used to measure the power output of power stations, generators, and other devices that produce electricity. For instance, the power capacity of a typical power plant is measured in megawatts (MW), where one megawatt equals one million watts.
Mechanical Systems
Watts aren’t just limited to electrical systems. They’re also used to measure the power output of mechanical systems like engines, turbines, and pumps. In these systems, wattage gives engineers a way to evaluate the efficiency of machines, ensuring they are optimized for performance.
For example, a car engine may be rated at several kilowatts of power, helping to compare different vehicles’ performance.
Watts in Renewable Energy
Watts are particularly important in renewable energy sources such as solar panels and wind turbines. Solar panels, for instance, have their energy output rated in watts or kilowatts, which tells you how much energy they can generate under ideal conditions.
A solar panel with a rating of 300W can produce 300 watts of power in full sunlight. By installing multiple panels, you can increase the total power output, measured in kilowatts.
Watts in Everyday Life
Lighting and Lumen Comparison
One area where watts have seen a change in relevance is with lighting. In the past, people chose light bulbs based on wattage, as higher-wattage bulbs provided more light. However, with the advent of energy-efficient lighting like LED bulbs, wattage is no longer a direct indicator of brightness.
Instead, lumens are now used to measure the brightness of a bulb, while wattage measures energy consumption. For example, a 10W LED bulb can provide the same brightness as a 60W incandescent bulb, using much less energy.
Smart Devices and Power Ratings
Modern gadgets like smartphones, tablets, and laptops have their power consumption measured in watts or kilowatts. As technology has advanced, devices have become more energy-efficient, consuming fewer watts while delivering higher performance.
Understanding the power rating of your devices can help you optimize your usage to extend battery life or reduce your electricity consumption.
Energy Efficiency and Watt Ratings
Energy Star and Appliance Efficiency
Energy Star is a program that promotes energy efficiency by certifying appliances that use fewer watts to achieve the same performance. Understanding the wattage of appliances allows consumers to make more informed decisions about the energy usage of their devices, potentially saving them money on their electricity bills.
Tips for Reducing Wattage Consumption
Reducing the number of watts your household consumes is not only beneficial for the environment, but it also reduces your energy bill. Here are a few tips:
- Switch to energy-efficient lighting like LED bulbs.
- Use smart thermostats to reduce the power consumption of HVAC systems.
- Unplug devices when not in use to avoid phantom power consumption.
Related Units and Variations
What is a Volt?
A volt is the unit of electrical potential difference or pressure that pushes the current through a conductor. Together with amperes, volts help determine the wattage of a device.
Amps and Ohms
Amperes (A) measure the flow of electric current, and Ohms (Ω) measure resistance. Understanding the relationship between volts, amps, and ohms is crucial for calculating wattage and ensuring that electrical systems operate safely and efficiently.
Why Understanding Watts is Important
For Consumers
Knowing how many watts your devices consume can help you choose energy-efficient appliances and make more informed decisions about your power consumption. This knowledge directly impacts your electricity bill, as reducing the number of watts used can lead to significant savings.
For Engineers
Engineers rely on watts to design and optimize mechanical and electrical systems. Whether it’s determining the power output of an engine or the energy requirements of a machine, watts provide critical information for system design.
For Environmentalists
Understanding wattage is essential for reducing energy consumption and transitioning to more sustainable energy sources. By using devices that consume fewer watts and relying on renewable energy sources like solar and wind, we can lower our carbon footprint and contribute to a greener planet.
Frequently Asked Questions About Watts
Is Higher Wattage Always Better?
No. Higher wattage doesn’t necessarily mean better performance. For example, LED bulbs use significantly less wattage than traditional incandescent bulbs while providing the same level of brightness.
What is the Relationship Between Watts and Power Bills?
Your electricity bill is calculated based on kilowatt-hours (kWh), which measures energy consumption over time. The more watts your devices use and the longer they operate, the higher your energy usage and bill will be.
How Are Watts Used in Solar Energy?
Solar panels are rated by the amount of power they can produce, measured in watts. Understanding these ratings helps homeowners and businesses decide how many panels they need to meet their energy requirements.
Conclusion
In summary, a watt is a fundamental unit of power that measures the rate at which energy is transferred or consumed. Its definition—one joule per second—applies across many fields, from electrical devices to mechanical systems. Understanding watts can help consumers manage energy usage, engineers optimize systems, and environmentalists promote sustainability. Whether you’re calculating your electricity bill or evaluating the efficiency of renewable energy systems, the watt is a key concept in understanding how power is used in our everyday lives.
Knowing more about watts and how they apply to the devices around you can help you make smarter choices, reduce energy consumption, and contribute to a more energy-efficient future.